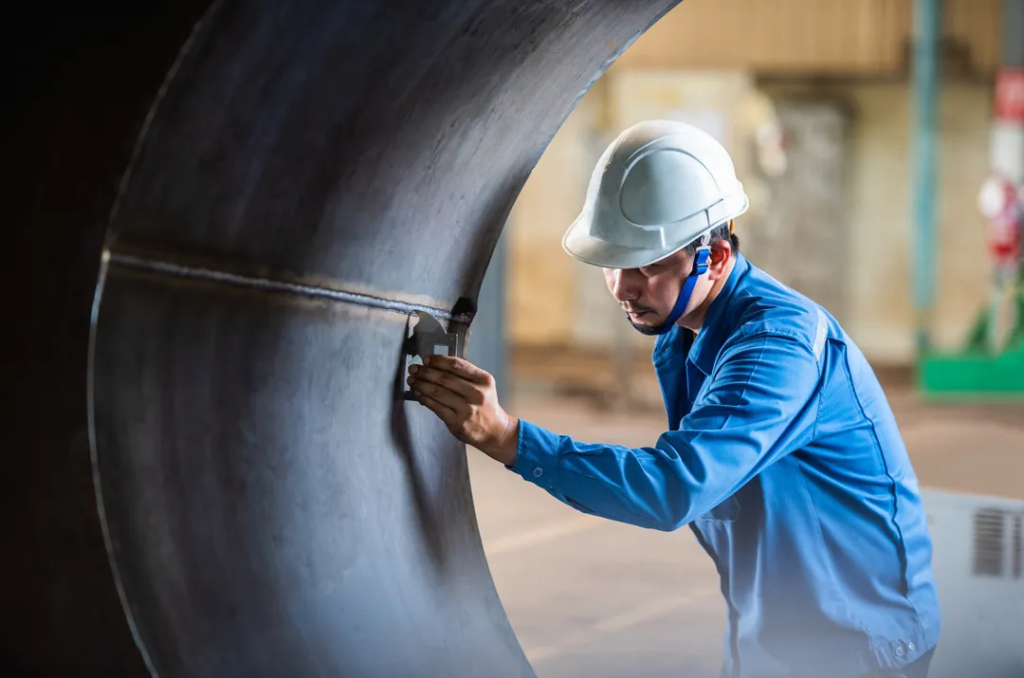
Beneath the ocean waves, the marine riser is crucial for offshore oil and gas operations.
I. Structure and Principle Made of high-strength alloy steel, it extends from the drilling platform to the seabed. The upper part links to the wellhead, the middle provides a drilling – fluid passage, and the bottom has sealing and fixing devices. It functions as a barrier, separating seawater from the high – temperature and high – pressure well environment. Drilling fluid circulates through it, cooling the bit, carrying cuttings, and maintaining well pressure.
II. Key Role in Oil and Gas Exploitation
1. Safety Assurance In the deep sea, high seawater pressure poses a threat. The riser, like armor, withstands this pressure. For instance, in the Gulf of Mexico’s deep – sea wells, it has endured over 1000 atmospheres of pressure, safeguarding drilling operations.
2. Circulation Stabilization Drilling fluid’s proper circulation is essential. The riser ensures this by preventing seawater intrusion, which could otherwise disrupt the fluid’s function and lead to accidents.
3. Efficiency Enhancement It reduces seawater – related drilling interruptions. In Brazil’s deep – sea pre – salt fields, advanced riser tech boosted exploitation efficiency by over 30%, cutting costs.
III. Technological Advancements
1. Material Innovation New materials like nickel – based alloys, with enhanced corrosion resistance, are replacing traditional steel, extending the riser’s lifespan.
2. Connection Improvement Advanced metal – to – metal sealing connections are being used, minimizing leakage risks at the connection points.
3. Intelligent Monitoring Sensors installed inside the riser enable real – time monitoring of pressure, temperature, and stress. Any anomalies trigger alarms, enhancing safety. In conclusion, the marine riser, a core part of offshore oil and gas equipment, is evolving. With continuous technological progress, it will further support global energy supply.